The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide to Cold Therapy
Why Cold Therapy Is Taking Over the Wellness World
Imagine stepping into an ice bath—your breath quickens, your skin tingles, and your body kicks into high alert. What might seem like pure shock to the system is actually an age-old wellness practice making a modern resurgence. Welcome to cold therapy (or cryotherapy), the art of using extreme cold to enhance physical and mental well-being. In this Ultimate Beginner Guide to Cold Therapy, we’ll explore how this powerful technique can be harnessed for better health and wellness, making it accessible for anyone new to the practice.
From elite athletes to biohackers and everyday wellness enthusiasts, people are turning to cold therapy for its proven health benefits. The science-backed perks include:
- Reducing inflammation and muscle soreness – A go-to for post-workout recovery.
- Boosting circulation and cardiovascular health – A cold plunge gets your blood pumping in ways that may improve heart function.
- Elevating mood and mental resilience – Cold exposure releases neurotransmitters that can help combat stress and anxiety.
- Strengthening the immune system – Some studies suggest it primes the body’s defenses (though more research is needed). For example, Bupa UK discusses how cold water therapy can help with recovery and its potential health benefits.
But before you rush to turn your shower dial to freezing, it’s crucial to understand how cold therapy works and how to practice it safely. The benefits are real, but so are the risks if done incorrectly. Let’s dive into the science behind cold therapy and what makes it such a powerful tool.
The Science Behind Cold Therapy: How the Body Reacts to the Cold
Cold therapy is more than just a test of willpower—it’s a physiological game-changer. Here’s what happens when your body is exposed to cold temperatures:
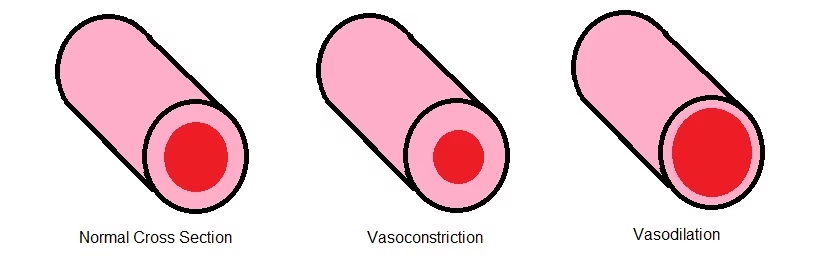
Vasoconstriction: The Body’s Survival Mode
The moment your skin senses extreme cold, your blood vessels constrict (vasoconstriction). This is your body’s natural defense mechanism to preserve heat and protect vital organs. Blood is pulled away from the extremities and redirected to the core, increasing circulation efficiency.
- This process helps reduce inflammation and swelling by limiting blood flow to injured or sore areas.
- When the body warms back up, vasodilation (blood vessel expansion) occurs, flushing out toxins and metabolic waste, speeding up recovery.
Endorphin Release: The Natural High
Cold exposure isn’t just about physical benefits—it supercharges your mood. When you endure cold temperatures, your brain releases a rush of endorphins (your body’s feel-good chemicals). Additionally, cold exposure increases norepinephrine levels, a neurotransmitter linked to:
- Enhanced focus and alertness
- Reduced stress and anxiety
- A natural antidepressant effect
Ever heard of the “cold plunge high”? That euphoric, energized feeling post-cold exposure is real—and it’s backed by science.
Metabolic Effects: Burning Fat and Boosting Energy
Cold exposure activates brown adipose tissue (BAT)—a type of fat that burns calories to generate heat. Unlike regular white fat, which stores energy, brown fat helps the body stay warm by burning calories. This process, called thermogenesis, may:
- Increase overall metabolism.
- Improve insulin sensitivity.
- Aid in weight regulation over time.
A Practice Rooted in History
While cold therapy seems like a new trend, it’s actually thousands of years old:
- Ancient Egyptians used cold applications to reduce pain and swelling.
- Hippocrates (the father of medicine) prescribed cold water therapy for various ailments.
- Nordic and Russian cultures have long practiced cold plunges, often pairing them with sauna use.
- Modern-day cryotherapy chambers use extreme cold (as low as -200°F/-130°C) for rapid, targeted exposure.
Today, science is catching up with ancient wisdom, proving what many have instinctively known for centuries: cold is a powerful force for healing, recovery, and mental clarity.
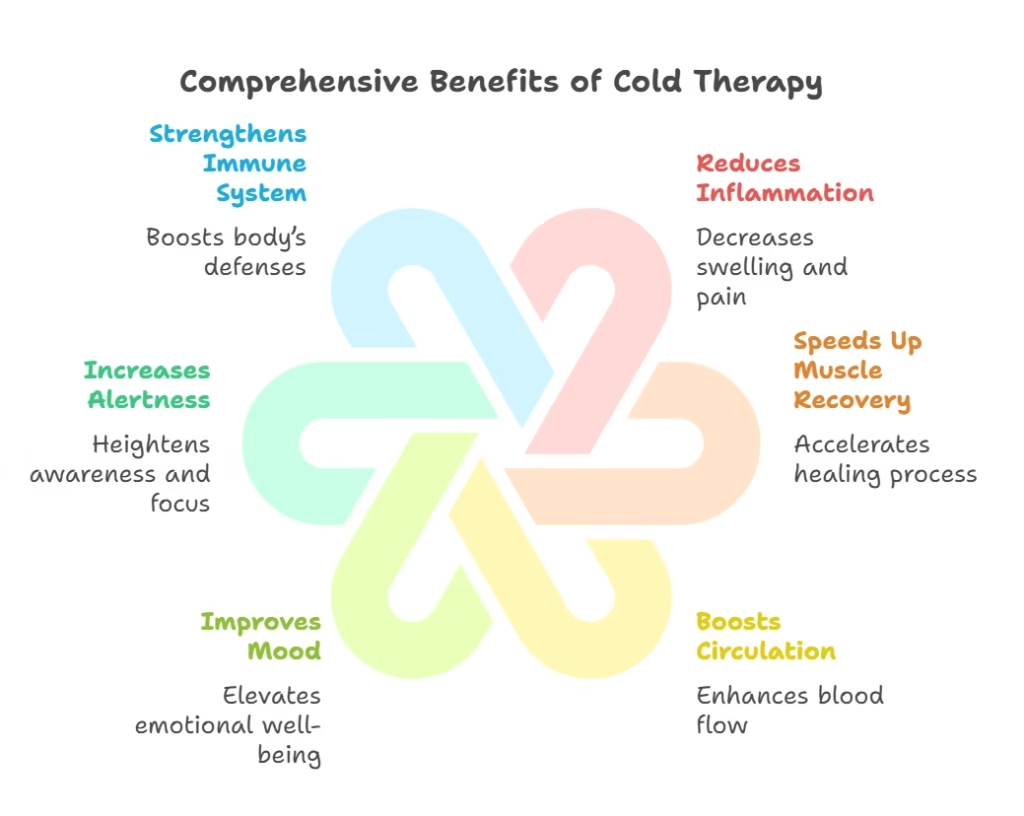
Benefits of Cold Therapy: Why Cold is the New Cool
Cold therapy isn’t just about embracing discomfort—it’s about unlocking a range of health benefits that optimize both body and mind. Here’s how strategic cold exposure can take your wellness to the next level.
Reduced Inflammation & Muscle Recovery: The Athlete’s Secret Weapon
If you’ve ever seen elite athletes dunking themselves in ice baths after a game, there’s a reason—it works. Cold therapy is a go-to recovery tool because it:
- Minimizes muscle soreness by slowing down inflammation and reducing swelling.
- Speeds up recovery by constricting blood vessels during exposure, then flushing out waste products like lactic acid when rewarming.
- Enhances performance longevity, allowing athletes to train harder and recover faster.
Whether you’re a pro athlete or just hit the gym hard, cold therapy can help keep muscle fatigue at bay and get you back in action quicker. For more in-depth information on the effects of cold water therapy, check out Dröm UK’s ultimate guide.
Cardiovascular Health Improvements: A Natural Circulation Boost
Cold therapy gives your heart and blood vessels a workout—without lifting a single weight. When exposed to the cold:
- Blood vessels constrict to conserve heat, then dilate upon warming, promoting better circulation.
- This repeated process may reduce chronic inflammation, which is linked to cardiovascular disease.
- Some studies suggest it lowers blood pressure and improves arterial function over time.
While cold therapy shouldn’t replace traditional heart-healthy habits, it can be a powerful supplement to a holistic cardiovascular wellness routine.
Mood & Mental Health Boost: A Shock to the System—In a Good Way
That post-plunge rush isn’t just in your head—well, actually, it is. Cold therapy floods your brain with feel-good chemicals like:
- Norepinephrine, which reduces stress and enhances focus.
- Endorphins, providing a natural mood boost similar to a runner’s high.
Regular cold exposure has been linked to:
✅ Reduced symptoms of depression and anxiety.
✅ Increased alertness and cognitive sharpness.
✅ A greater ability to handle stress (cold therapy trains your nervous system to stay calm under pressure).
Think of it as mental toughness training for your nervous system—with a side of mood enhancement.
Strengthening the Immune System: Can Cold Keep You Healthy?
The idea that cold exposure trains the immune system has been around for centuries, but does science back it up? Here’s what we know:
- Some research suggests cold exposure increases white blood cell activity, potentially helping the immune system respond more efficiently.
- A study on people practicing cold showers, meditation, and breathwork (like the Wim Hof Method) showed a stronger immune response to infections.
- However, more research is needed to confirm long-term immune-boosting effects.
While anecdotal evidence is strong, the scientific jury is still out. That said, many cold therapy enthusiasts swear by fewer colds, improved energy levels, and a stronger immune response over time.
Risks and Precautions: When Cold Gets Too Cold
Cold therapy is powerful, but it’s not without risks. Understanding these potential dangers can help you reap the benefits safely.
Cold Water Shock: The Body’s Instant Panic Mode
Jumping into icy water might sound exhilarating, but it can trigger a dangerous shock response, especially for beginners. The body reacts with:
- Rapid breathing (hyperventilation)
- A sudden spike in heart rate and blood pressure
- Potential dizziness or panic
For those with heart conditions or high blood pressure, this can be risky. To minimize the danger:
✅ Start with gradual exposure (cool showers before plunges).
✅ Control your breathing—deep, slow breaths help regulate the shock response.
✅ Never jump into freezing water suddenly, especially without experience.
Hypothermia and Overexposure: When Cold Turns Dangerous
Staying in icy water too long can lead to hypothermia, a condition where the body loses heat faster than it can produce it. Symptoms include:
⚠️ Uncontrollable shivering.
⚠️ Confusion, slurred speech, or dizziness.
⚠️ Numbness, pale or blue skin.
To stay safe:
- Keep sessions between 2–10 minutes at first, adjusting based on comfort.
- Use water temperatures around 10°C to 15°C (50°F to 59°F) for safe immersion.
- Always have warm clothing and a heat source ready post-session.
Cardiovascular and Respiratory Stress: Who Should Avoid Cold Therapy?
Cold exposure can be taxing on the heart, lungs, and blood vessels. It’s best to avoid or consult a doctor first if you have:
🚫 Heart disease or high blood pressure (cold shock can spike heart rate).
🚫 Asthma or respiratory conditions (cold water can trigger breathing issues).
🚫 Poor circulation or Raynaud’s disease (cold can restrict blood flow too much).
If you have a medical condition, safety first—speak with a healthcare professional before diving in. For more on the risks associated with cold water immersion, read American Heart Association’s article on the dangers of cold water immersion.
Getting Started with Cold Therapy (Safely!)
Diving headfirst into an ice bath sounds hardcore, but when it comes to cold therapy, slow and steady wins the race. Proper acclimatization and safety precautions will help you maximize benefits while minimizing risks. If you’re curious about why doctors recommend ice baths and how cold therapy fits into the broader wellness world, be sure to check out our earlier post, Do Doctors Recommend Ice Baths?
Gradual Acclimatization: Easing Into the Cold
If you’re new to cold exposure, don’t shock your system all at once—adaptation is key. Here’s how to start:
✅ Cold Showers First: Begin with 30 seconds of cold water at the end of your regular shower, gradually increasing the time over a few weeks.
✅ Lower the Temperature Gradually: Reduce the water temp in increments, rather than going straight to freezing.
✅ Move to Ice Baths: Once comfortable with cold showers, try a short immersion (1-2 minutes) in a cold tub (around 10°C to 15°C).
✅ Outdoor Exposure: Walking in cool air with minimal clothing can also help your body adapt to lower temperatures.
Patience is everything—over time, your body will build cold tolerance and improve its ability to regulate heat.
Essential Safety Measures: Cold, But Cautious
Cold therapy can be highly beneficial, but only when done safely. Follow these precautions:
🔹 Check with a Doctor First: If you have heart disease, respiratory conditions, or high blood pressure, get medical clearance before trying cold exposure.
🔹 Warm-Up & Cool-Down: A short warm-up before exposure (like light movement) helps prepare your body, while a gradual cool-down afterward prevents sudden temperature shifts.
🔹 Never Go Solo: Especially for cold plunges, have a buddy present—cold water shock can cause dizziness or disorientation.
🔹 Have an Emergency Plan: Keep warm clothes, a blanket, and a hot drink nearby in case of excessive cooling or hypothermia symptoms.
Cold exposure is a stress on the body—but the goal is to control the stress, not push too far too fast.
Optimal Water Temperatures and Exposure Times
How cold is too cold? It depends on experience level, but here are general guidelines:
🌡 Recommended Temperature Range: 10°C to 15°C (50°F to 59°F)—cold enough to trigger benefits without excessive risk.
⏳ Suggested Duration: Start with 2-3 minutes and work up to 5-10 minutes over time. Never stay in longer than your body can safely handle.
🚀 Listen to Your Body: If you feel numbness, dizziness, or excessive shivering, exit the water immediately.
Post-Therapy Recovery: Warming Up the Right Way
After an intense cold session, your body needs time to naturally reheat. Here’s how to recover properly:
✅ Warm Clothing: Dry off and put on warm layers immediately.
✅ Gentle Movement: Light stretching or walking helps generate internal heat.
✅ Hot Drinks, Not Hot Showers: A warm (not scalding) beverage aids recovery, but jumping into a hot shower too soon can cause blood pressure fluctuations and dizziness.
Gradual warming allows your body to return to homeostasis safely—so resist the urge to crank up the heat right away.
Chill Responsibly
Cold therapy is a game-changer, but like any powerful tool, it requires respect and knowledge.
🔹 The Benefits? Faster recovery, better circulation, stronger immunity, and a mental resilience boost.
🔹 The Risks? Cold shock, hypothermia, and cardiovascular stress—especially if done carelessly.
🔹 The Key to Success? Gradual adaptation, proper safety measures, and listening to your body.
Approach cold therapy with patience and awareness, and you’ll unlock its full potential while staying safe. And remember—if you have any underlying health conditions, talk to your doctor first before diving in.
Ready to take the plunge? Start small, stay consistent, and let the cold work its magic. ❄️🔥
FAQ
1. What is cold therapy?
Cold therapy, or cryotherapy, involves exposing the body to cold temperatures to promote recovery, reduce inflammation, and boost mental clarity. It includes methods like ice baths, cold showers, and cryotherapy chambers.
2. Is cold therapy safe for everyone?
Cold therapy can be safe for most people, but it’s important to start slowly and consult with a healthcare professional if you have heart conditions, high blood pressure, or other health concerns.
3. How long should I stay in cold therapy?
For beginners, aim for 2–3 minutes in cold water or a cold shower. Over time, you can gradually increase the exposure to 5–10 minutes depending on comfort levels and tolerance.
4. Can cold therapy help with muscle recovery?
Yes! Cold therapy is often used by athletes to reduce muscle soreness and inflammation after intense physical activity, speeding up recovery.
5. What are the benefits of cold therapy?
Cold therapy can help reduce inflammation, improve circulation, boost mood, enhance mental resilience, and strengthen the immune system.

